1. Change the user permissions of the file and note the changes after ls -ltr
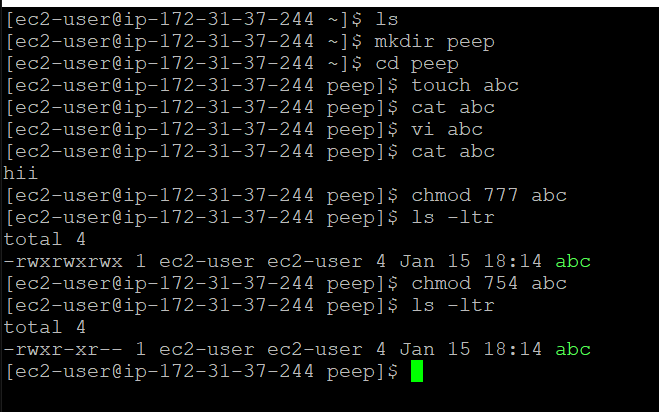
Here you can see the file abc has permission 777 that means it has all the read, write and execute permissions.
And below I have changed the permission to 754 that explaination has been given in the second point.
2. Write an article about File Permissions based on your understanding from the notes.
In Linux, file permissions determine who can read, write, and execute a file. Each file and directory has a set of permissions that specify which users or groups can perform certain actions. These permissions are represented by a combination of letters and symbols, such as -rwxrw-r — , that indicate the owner, group, and others’ permissions for a file or directory. The three types of permissions are:
Read (r): Allows a user to view the contents of a file or list the contents of a directory
Write (w): Allows a user to modify or delete a file or add, remove, or rename files in a directory
Execute (x): Allows a user to run a file as a program or script
Each file and directory also has an owner, which is the user who created it, and a group, which is a set of users with similar permissions. The permissions can be set or changed using the chmod command, and the ownership can be set or changed using the chown command.
Numeric permission in Linux
In Linux, file permissions are represented by a set of three digits, referred to as the “numeric permission.” These digits represent the permissions for the owner of the file, the group owner of the file, and all other users, respectively.

Each digit is a combination of the values 4 (read), 2 (write), and 1 (execute), with a value of 7 indicating full permissions (read, write, and execute), a value of 6 indicating read and write permissions, and so on.
For example, a numeric permission of 755 would give the owner full permissions, the group owner and all other users read and execute permissions.
3. Read about ACL and try out the commands getfacl and setfacl
ACL stands for Access Control List. It allows the user to give a more specific set of permissions to a file or directory without changing the base ownership and permissions. Properly managing access control permissions in Linux is crucial for maintaining security, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring that only authorized users can access and modify files and directories.
getfacl Command-:The getfacl command is used to retrieve the ACL information for a file or directory. It displays the detailed ACL entries, including any extended permissions beyond the standard owner, group, and others permissions.
Syntax-: getfacl <name of file or directory> to check acl permission.
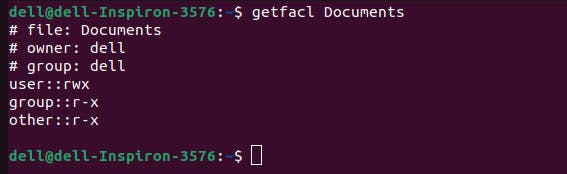
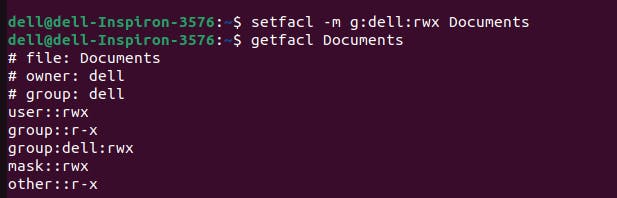
Setfacl Command-:The setfacl command is used to set or modify ACL entries for files and directories. It allows users to define custom permissions for individual users or groups, providing more flexibility in access control.
Syntax-:setfacl <OPTIONS> <name of file or directory>to set or modify the ACL entries.
ex-: To set a read write and execute permission specific for group "dell"-
To remove the specific permission on the group "dell"-
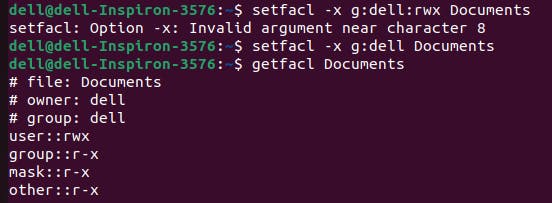
To remove all ACL permissions -
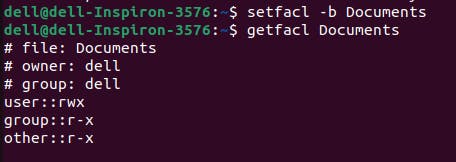
to see whether the permission was removed or not type ls -l
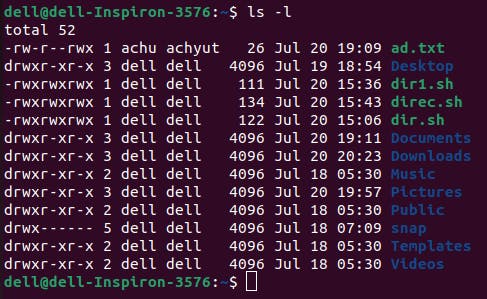
Here in this picture '+' sign was removed which means permission was removed successfully.
